The Lucy statistical rectification method allows one to uncover the intrinsic distribution of data from its observed distribution. In this ApJ Letter, I apply the method to build the Tully-Fisher relation of disk galaxies, where both axes of the correlation (magnitude and emission line widths) are affected by the inclination angles of the disks’ rotation axes towards us. The main advantage of the statistical method compared to the conventional method is that it eliminates one major source of uncertainty in the process: inclination angle estimation from axial ratio.
The data set I used is from the Arecibo wide-area survey of nearby galaxies called ALFALFA. The results are shown in the two figures below.
Although this Letter deals with only the Tully-Fisher relation, the statistical rectification method could be easily adapted to restore the intrinsic distributions from, e.g., the observed color-magnitude diagram of galaxies, the black hole mass vs. Eddington-ratio diagram of active galactic nuclei, etc. Indeed, it can be applied to any problems where (1) the observed properties can be converted from the intrinsic pfroperties by a relation that involves a “hidden” parameter and (2) the probability density function of the hidden parameter is precisely known.
Bibliography: Fu, H., ApJL, 963, L19 (2024) “Restoration of the Tully-Fisher Relation by Statistical Rectification” The Python notebook that implemented the method and the merged data catalog are shared on Github.
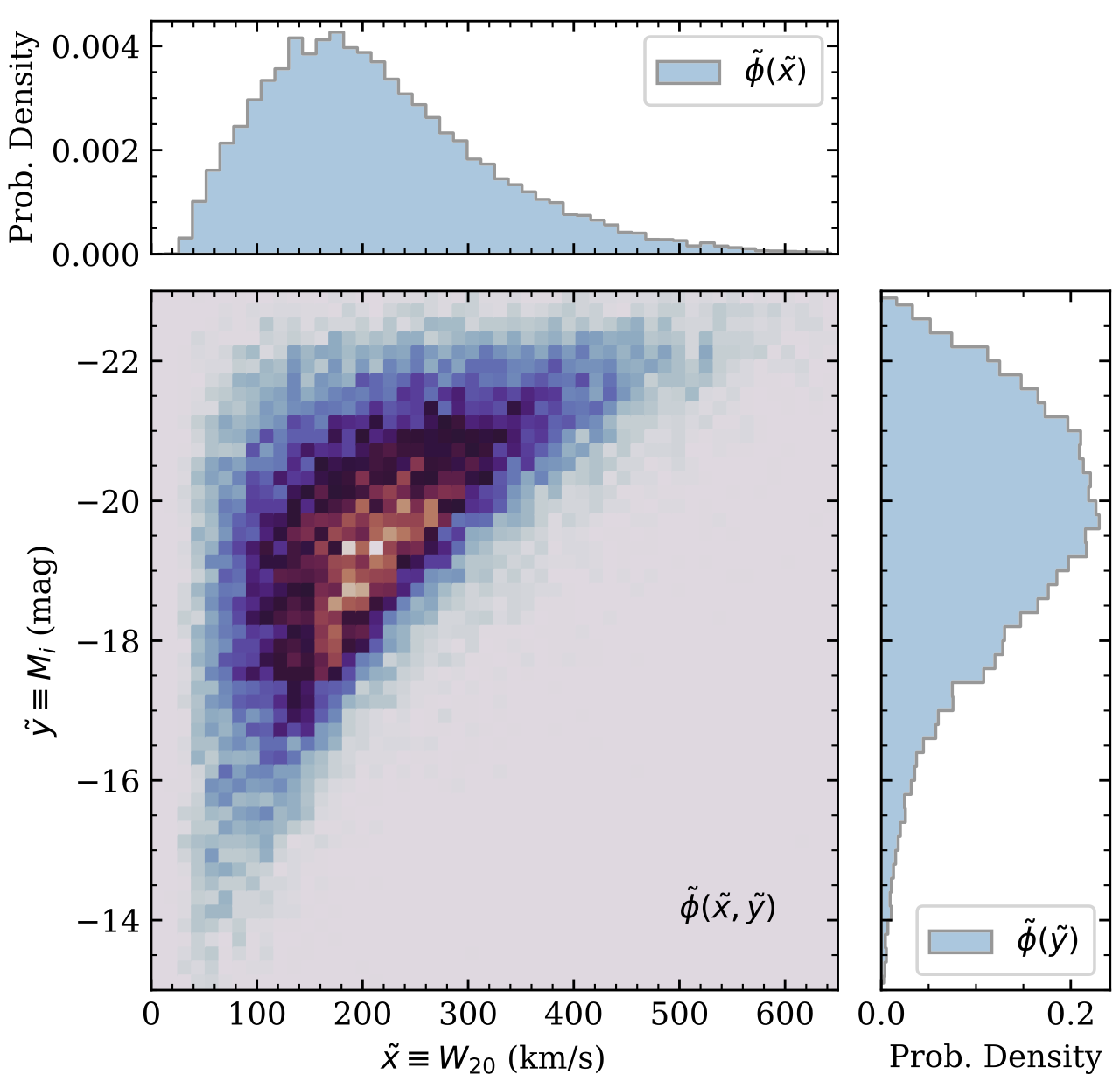 Above: The observed distribution of ALFALFA-SDSS galaxies in the
plane of projected i-band absolute magnitude vs. projected HI line width.
Above: The observed distribution of ALFALFA-SDSS galaxies in the
plane of projected i-band absolute magnitude vs. projected HI line width.
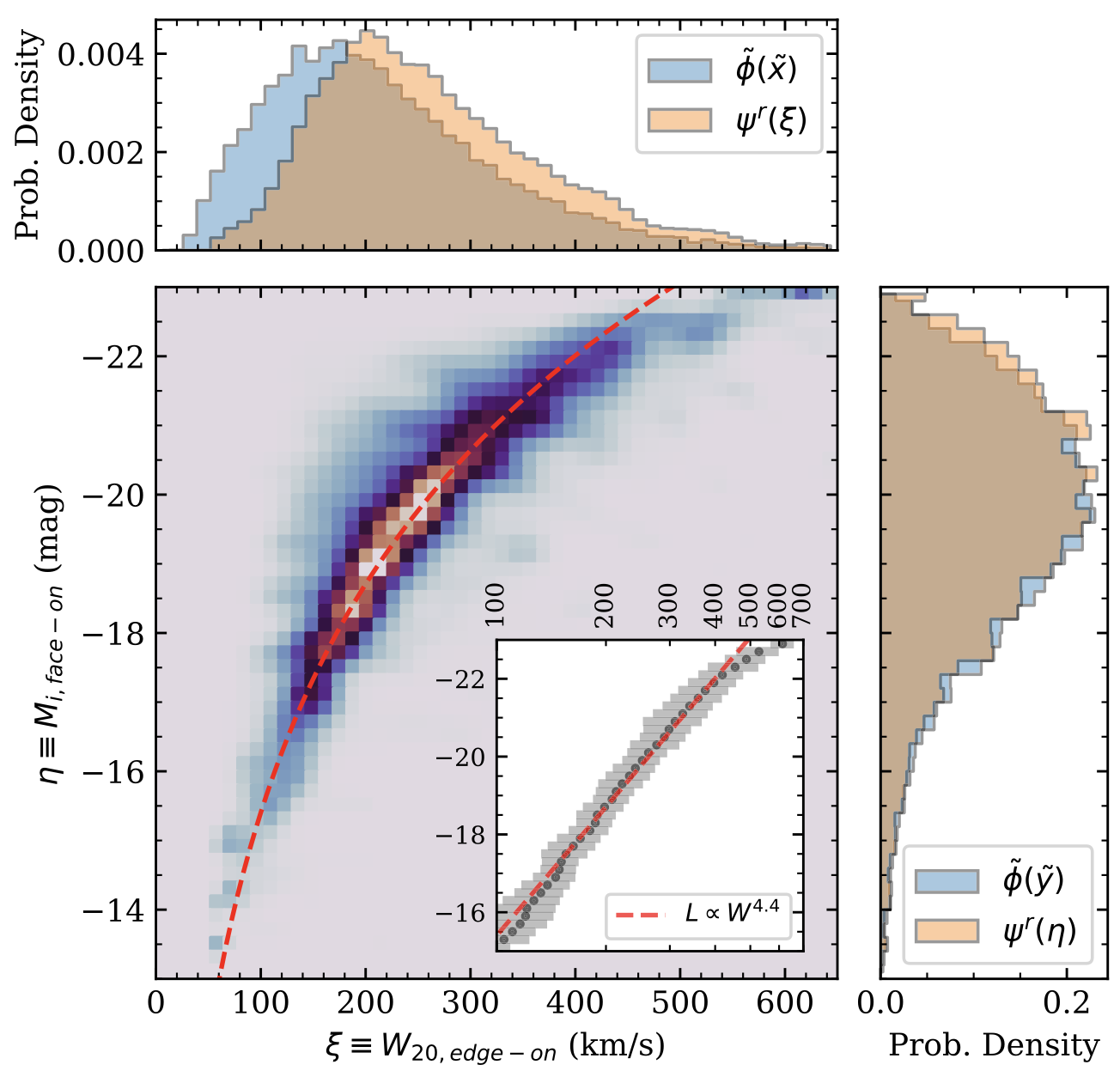 Above: The statistically restored distribution of the ALFALFA-SDSS galaxies in
the plane of face-on i-band absolute magnitude vs. edge-on HI line
width. This is the Tully-Fisher relation.
Above: The statistically restored distribution of the ALFALFA-SDSS galaxies in
the plane of face-on i-band absolute magnitude vs. edge-on HI line
width. This is the Tully-Fisher relation.
Acknowledgement
The research benefited from the excellent data from two ground-based observational facilities: the Arecibo Observatory and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The work at Iowa was generously supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under grant AST-2103251.