(1) A rotation curve of a galaxy is a plot of orbital speed versus galactocentric distance. Let's consider an elliptical galaxy, that can be roughly considered spherically symmetric. Assume the density as a function of galactocentric distance ![]() can be described as follows.
can be described as follows.
| (1) | |||
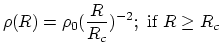 |
(2) |
(2) Problem 2.9 from textbook.
(3) Problem 2.10
(4) Problem 2.11
(5) Problem 2.13 (I recommend you use MathCad in solution of this problem.)
(6) Problem 2.14 (I recommend you use MathCad in solution of this problem.)
(7) In lecture, I showed how elliptical orbits could be derived from Newton's Laws. In the course of that derivation, a vector ![]() emerged, defined by the equation (check class notes)
emerged, defined by the equation (check class notes)
| (3) |
(8) Here is one to let you appreciate how special the inverse square law of gravity is for our existing here in the universe. An object is subject to a central force, and moves on an orbit given by
| (4) |